Photography Golden Triangle
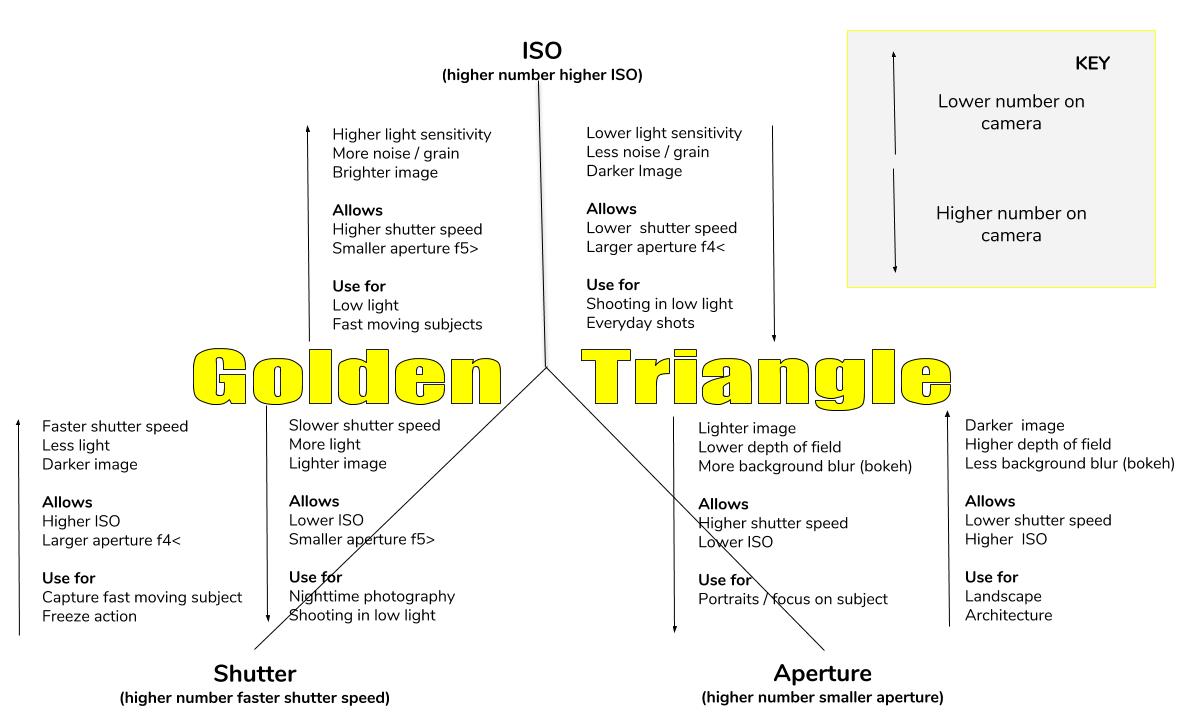
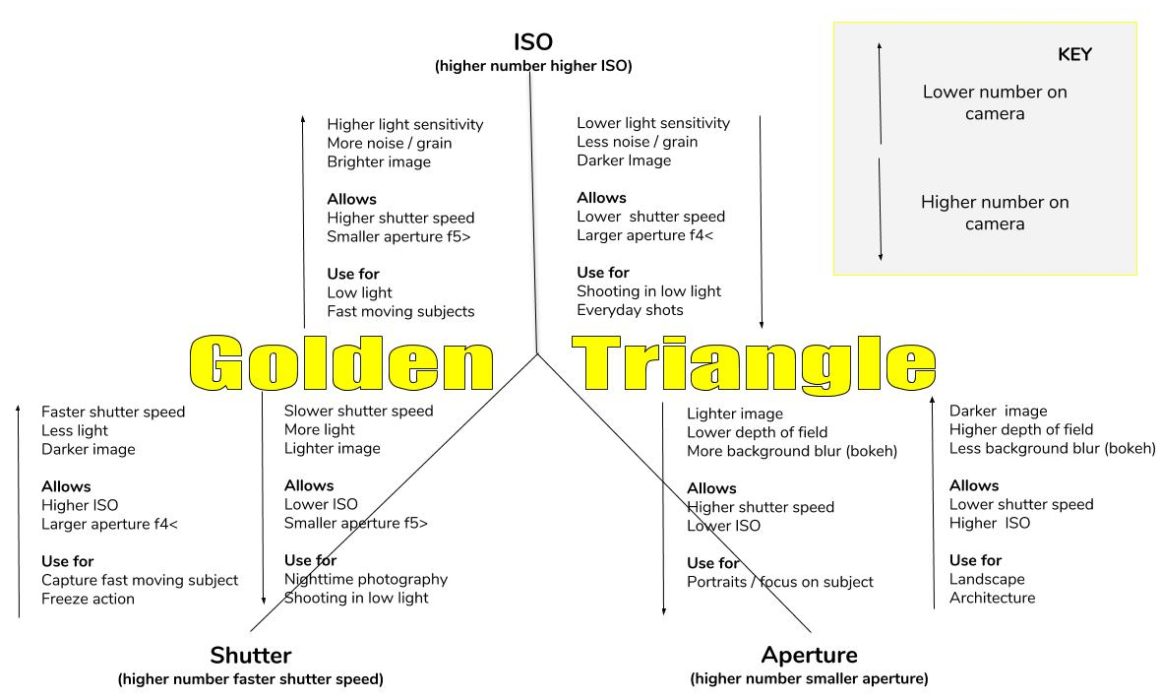
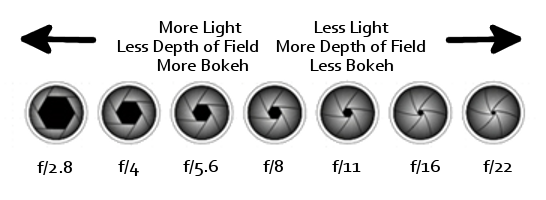
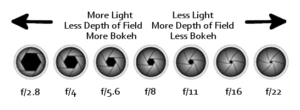
One of the most confusing areas in photography has to be what is known as The Golden Triangle or The Three Pillars of Photography, this being ISO, Aperture and Shutter Speed. I get tons of questions about trying to get out of Auto and move into Manual mode.
The simple way to use these to change your photography is remember this simple statement
“You change one, you change them all”
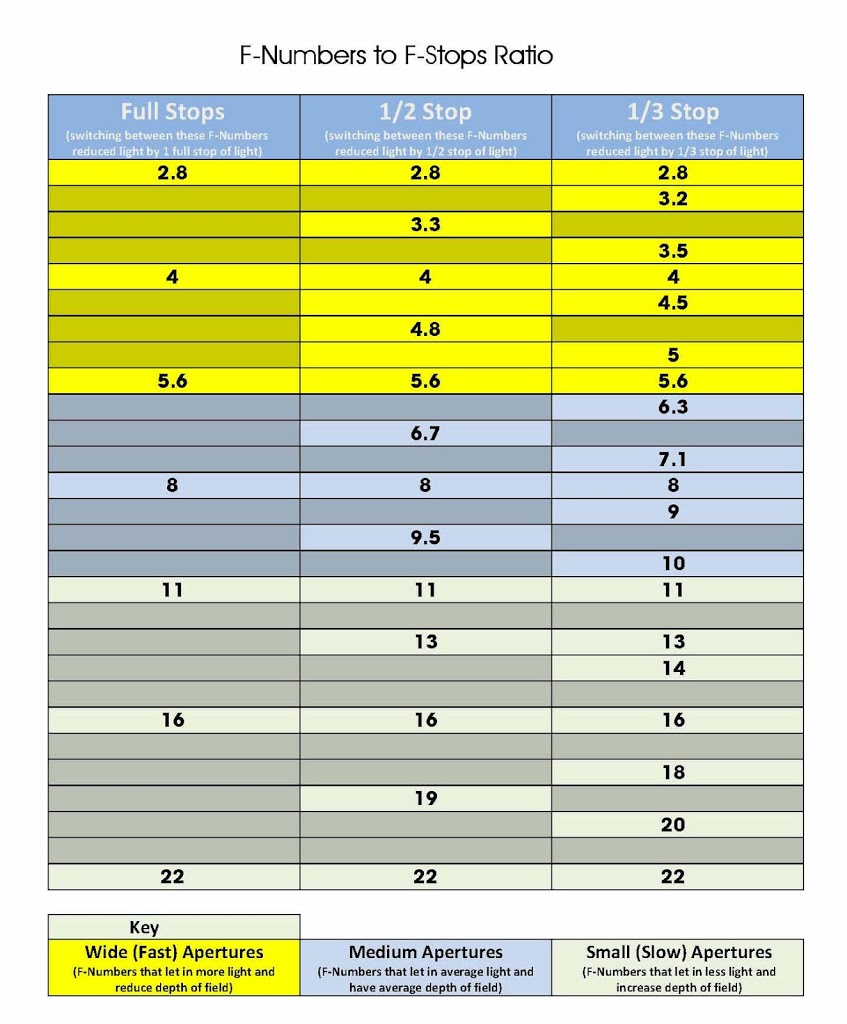
This post is a guide to exactly what ISO, Aperture and Shutter Speed are and what they do and how they effect your photos, plus the relationship between them. Plus as a little bonus I have drawn up a chart for you to download and keep to help you in the field or where ever you need a quick reminder.
In order to make it a bit easier to understand the relationship between ISO, Aperture and Shutter Speed I have drawn up a simply diagram below. If you would like to download a copy to use in the field or for you own use,please use the buttons below.